The Heart Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Muscular Tissue Emedicodiary
The intercalated disc (ID) is a highly specialized structure that connects cardiomyocytes via mechanical and electrical junctions. Although described in some detail by light microscopy in the 19th century, it was in 1966 that electron microscopy images showed that the ID represented apposing cell borders and provided detailed insight into the complex ID nanostructure. Since then, much has been.

Anatomy and Physiology I Muscle Structure and Contraction
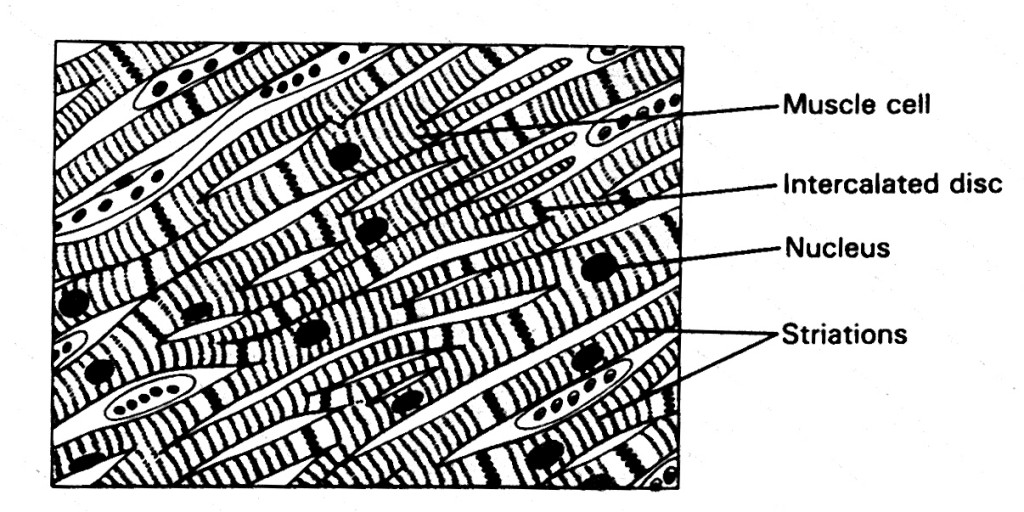
CH. 10 study guide. Get a hint. how do cardiac muscles differ from skeletal muscle cells? Click the card to flip 👆. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle is striated, but the bundles are connected at branching, irregular angles called intercalated discs.
[Figure, Heart muscles, cardiac muscle, intercalated...] StatPearls
Introduction. Cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. However, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control.

Structure And Function Of Muscle And Nerves Lab
Skeletal muscle can not do this. Even though cardiac muscle has autorhythmicity, heart rate is modulated by the endocrine and nervous systems.. Cardiac muscle cells branch freely. A junction between two adjoining cells is marked by a critical structure called an intercalated disc, which helps support the synchronized contraction of the.
intercalated discs function
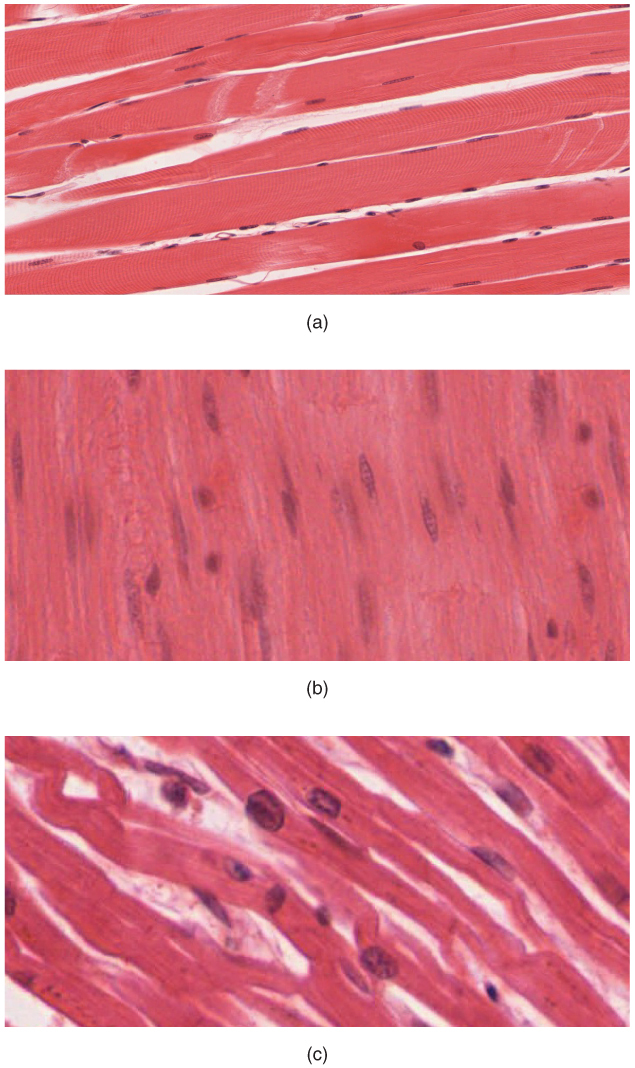
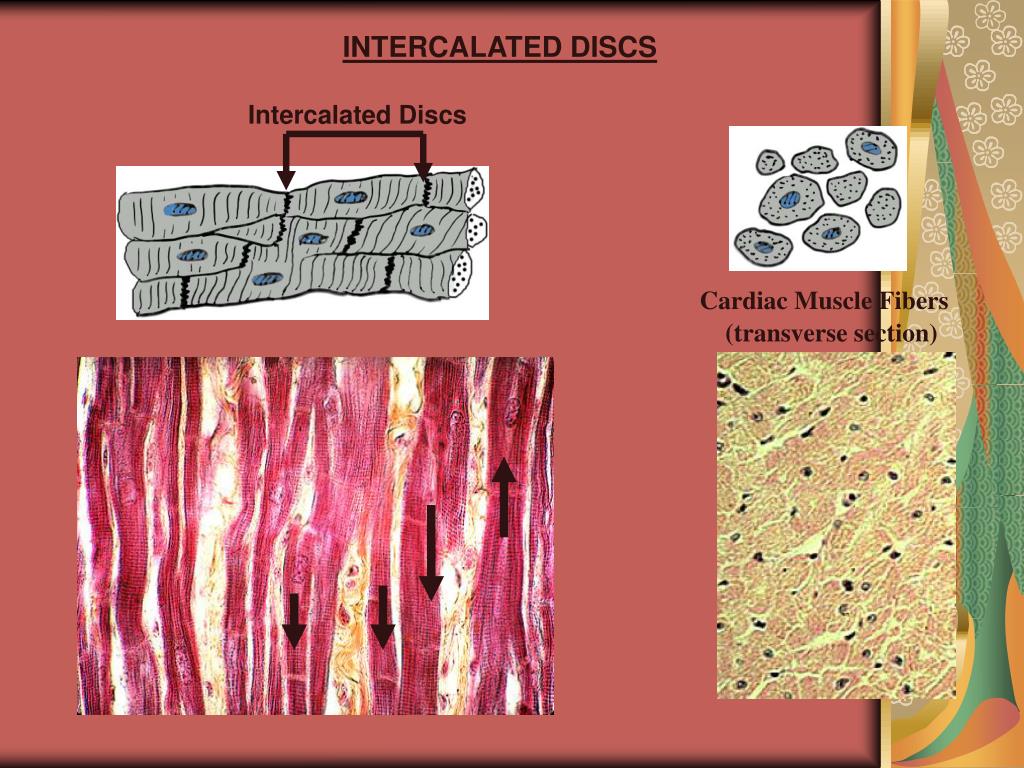
There are artifactual transverse breaks in some of the muscle fibers, which are NOT intercalated discs. Intercalated discs are also fairly easy to find in the areas where muscle fibers are longitudinally oriented in slide 98-1 #098-1 Webscope and/or slide 98-N #098N Webscope (be sure to look at both H&E and trichrome-stained sections).

Farone Exam 4 Cardio Biology 346 with Farone at Grove City College
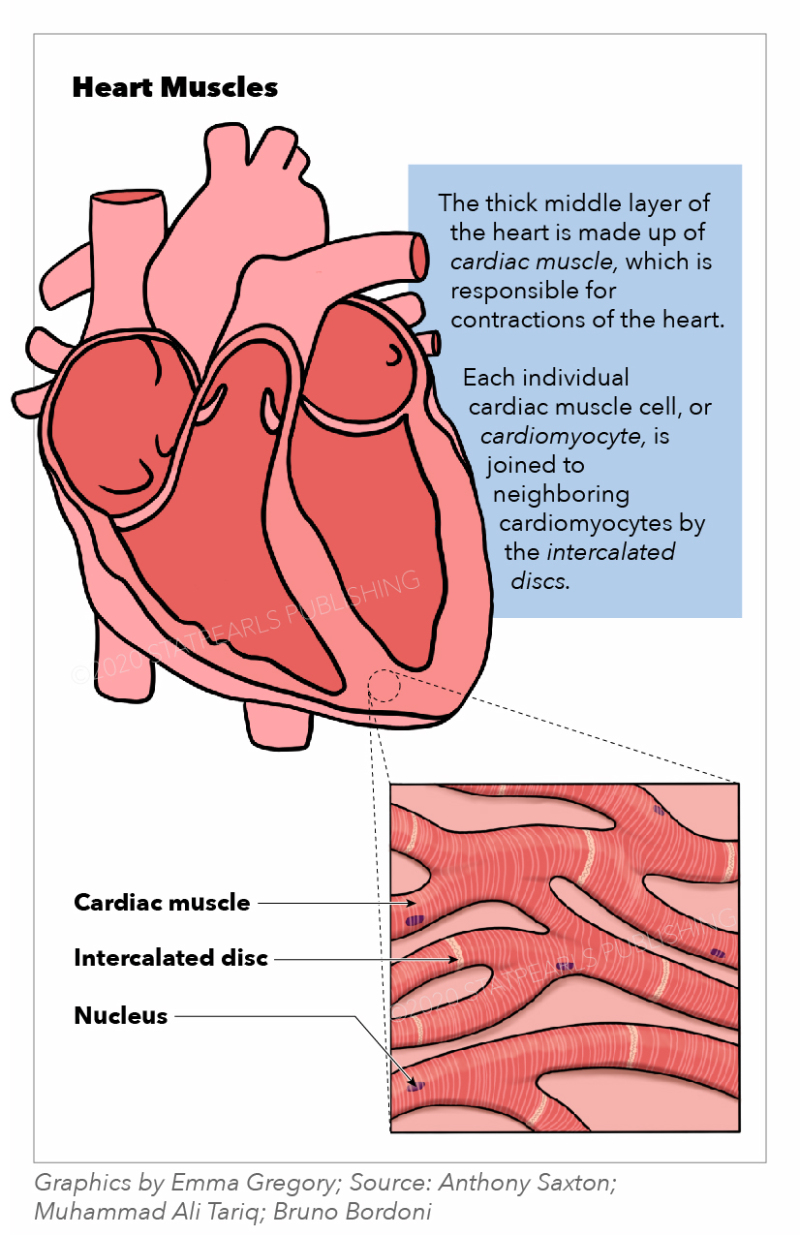
Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. It is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (AKA visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. Coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. Cardiomyocytes are the.

Function Of Intercalated Discs In Heart Muscle slidesharetrick
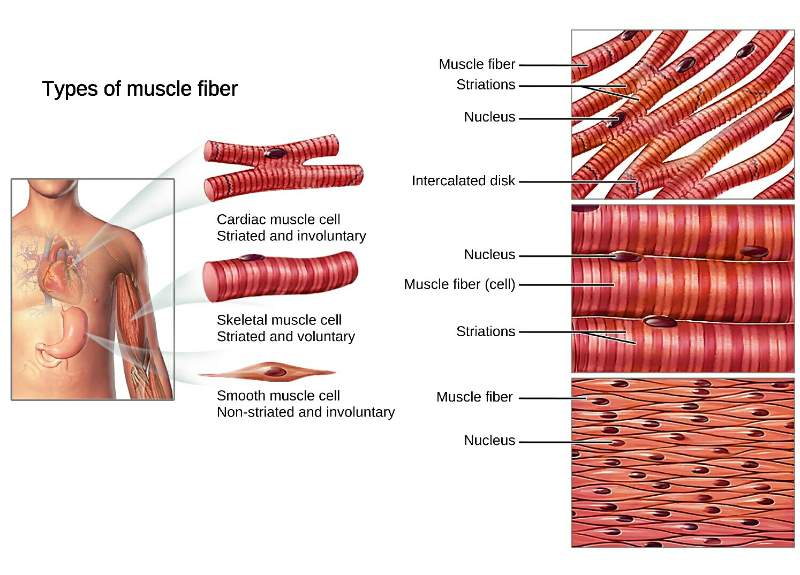
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (Figure 1).
Types of Muscle Tissue Physiology Geeky Medics
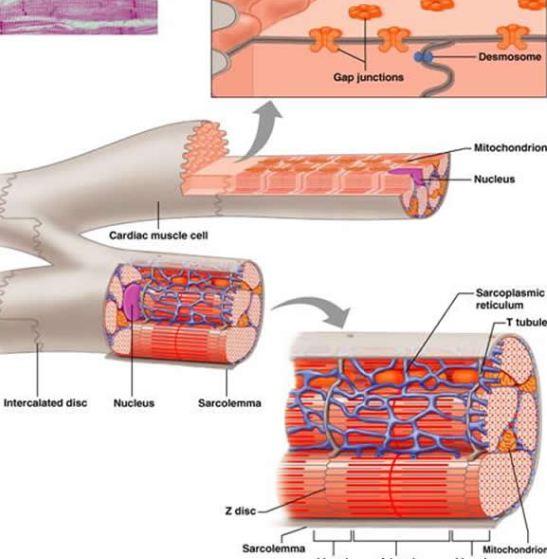
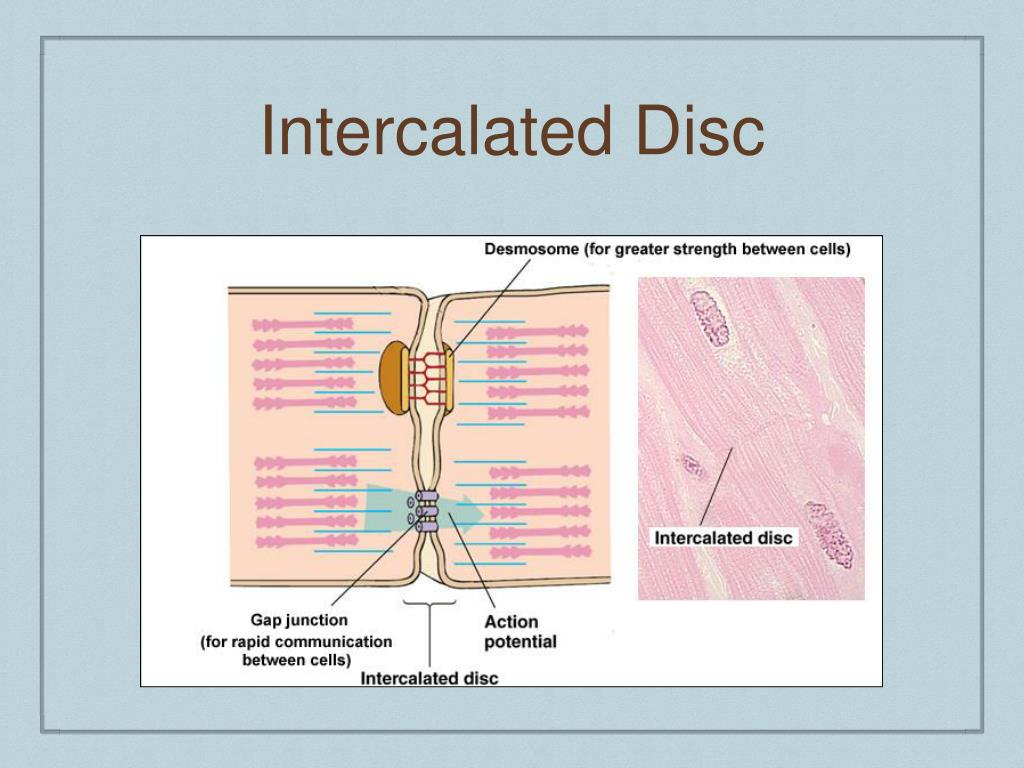
Cardiac muscle is striated muscle that is present only in the heart. Cardiac muscle fibers have a single nucleus, are branched, and joined to one another by intercalated discs that contain gap junctions for depolarization between cells and desmosomes to hold the fibers together when the heart contracts. Contraction in each cardiac muscle fiber.
Intercalated discs Location, Function, FAQs and Pictures
Intercalated discs are unique features found in cardiac muscle cells, which allow for the rapid transmission of electrical signals and synchronized contraction of the heart. Skeletal muscles do not contain intercalated discs.

Cardiac muscle Veterinary Histology
Cardiac cells are special, amongst the muscle types, because they are connected to each other by intercalated discs - structures that are only found in cardiac muscle cells. These can be seen in this diagram, as darkly staining irregular lines, at 90 degrees to the striped sarcomeric pattern.. Skeletal muscle does not have any cell-cell.
The Heart Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
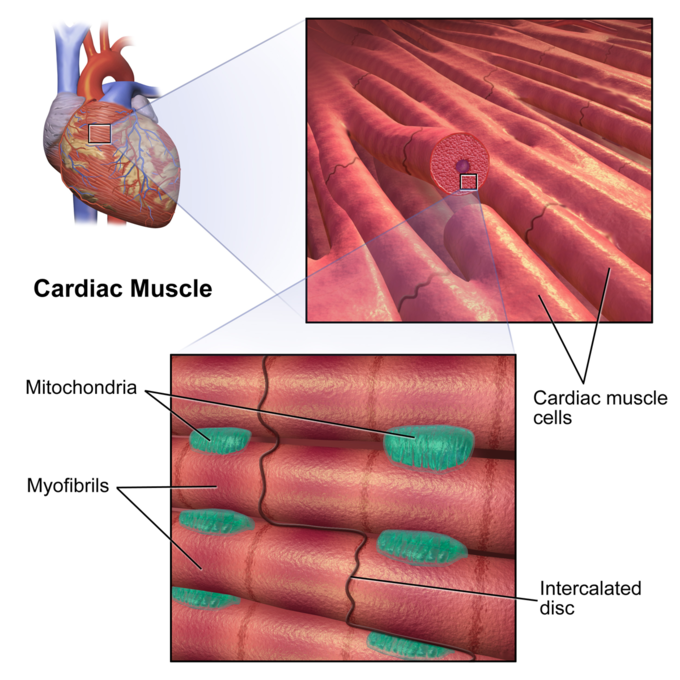
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells ( cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional syncytium. By contrast, skeletal muscle consists of multinucleated muscle fibers and exhibits no intercalated discs.
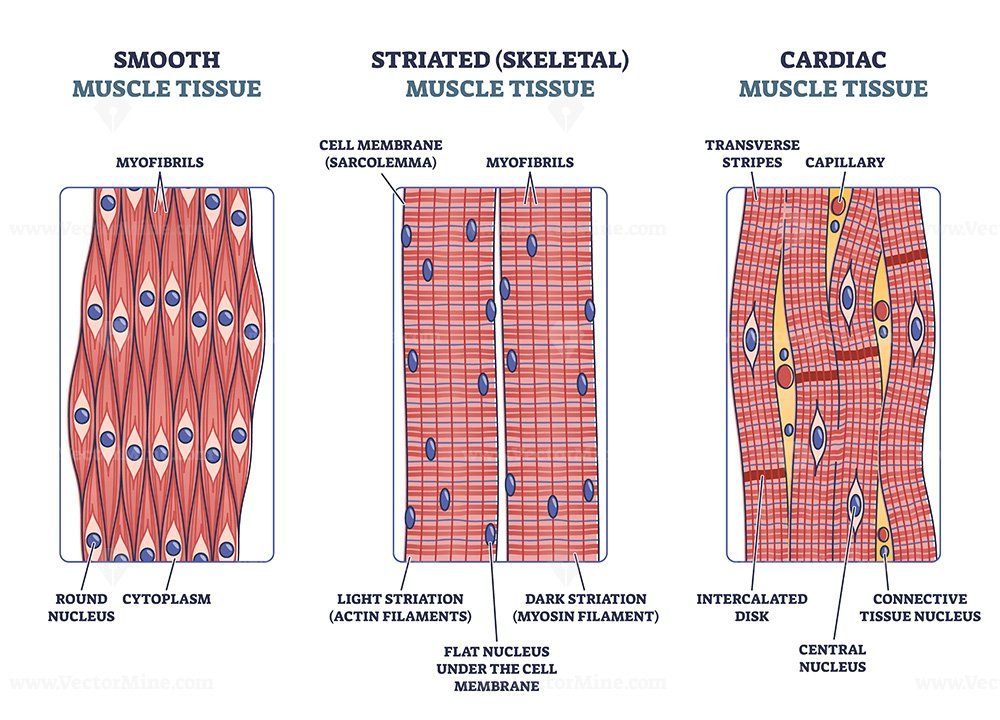
Diagram Of Striated Muscle
The remainder of the intercalated disc is composed of desmosomes. A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (Figure 2). Figure 2. Cardiac Muscle. Intercalated discs are part of the cardiac muscle sarcolemma and they.
PPT Basic Cardiology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID612474
Intercalated discs play a vital role in holding cardiac muscle cells together using the fascia adherens and desmosomes. The increased surface area of the finger-like extensions of cell membrane provides ample room for these connections to form. Gap junctions allow ions to pass from one cardiac muscle cell to another, providing an extremely fast.
PPT Cardiac Muscle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6182155
Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. Figure 10.21 Cardiac Muscle Tissue Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. LM × 1600.

17.3 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity Medicine LibreTexts
Skeletal muscle is a voluntary type of muscle that acts upon the skeletal system by pulling on the bones and allowing body movements.. The fibers are crossed by linear bands called intercalated discs. These structures have two important roles. Firstly, they provide attachment points that provides the tissue with a characteristic branched.

intercalated disk Histology
The intercalated disc (ID) mediates coupling of neighboring myocytes through intercellular signaling. Intercellular communication is highly regulated via intracellular signaling, and signaling pathways originating from the ID control cardiomyocyte remodeling and function. Herein, we present an overview of the inter- and intracellular signaling.