Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
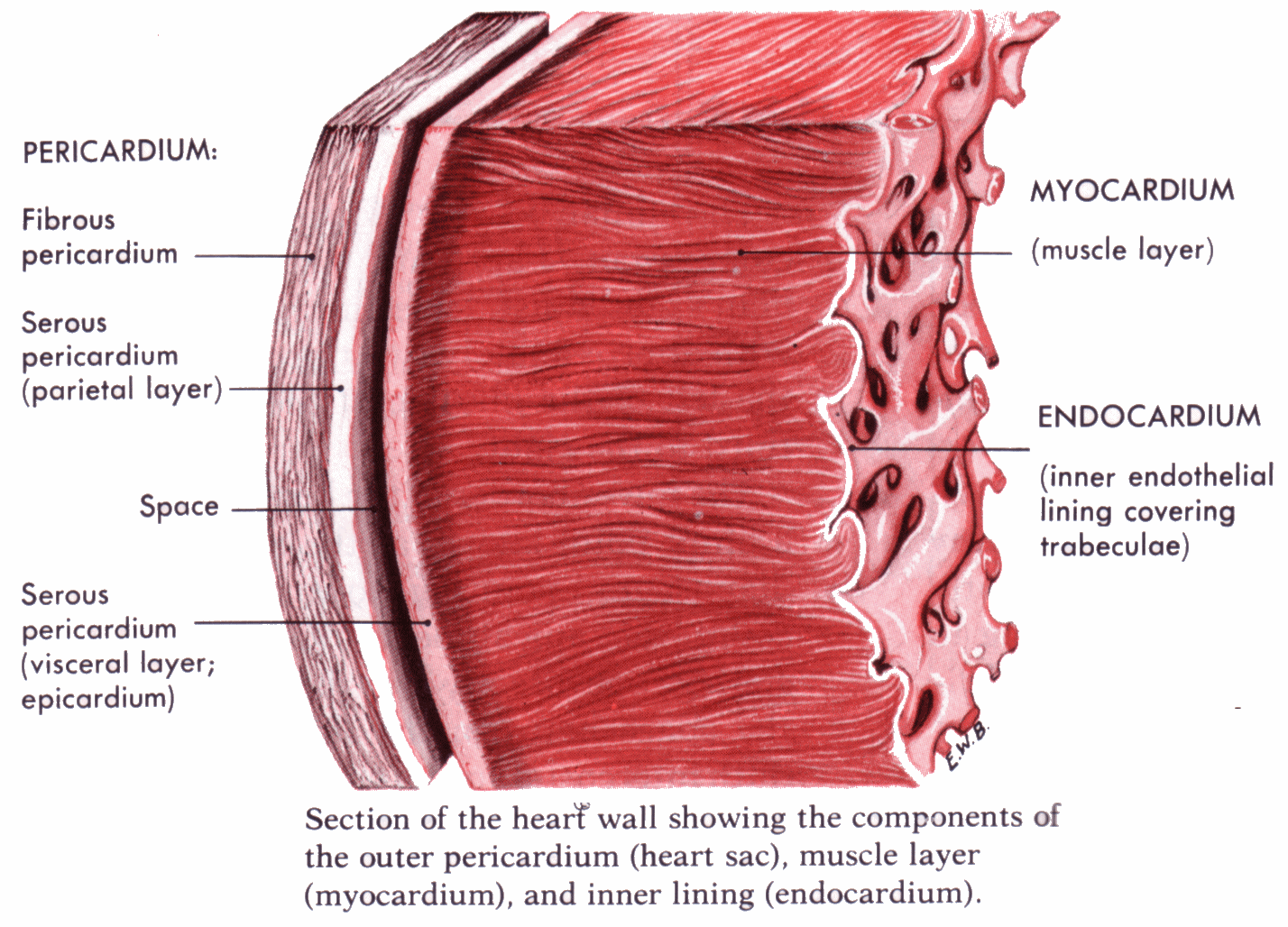
Which is the cardiac muscle layer of the heart? Socratic
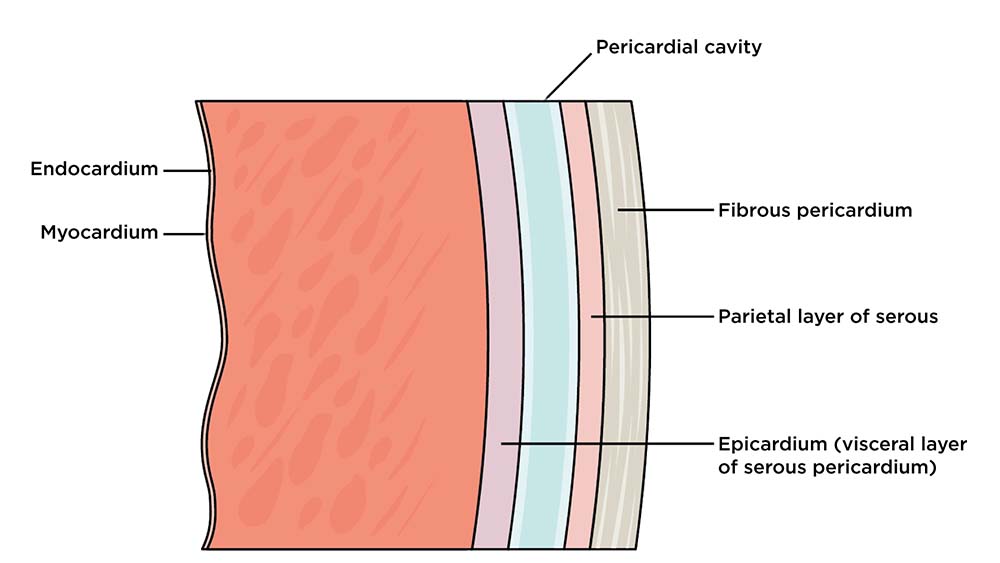
The muscular wall of the heart has three layers. The outermost layer is the epicardium (or visceral pericardium). The epicardium covers the heart, wraps around the roots of the great blood vessels, and adheres the heart wall to a protective sac. The middle layer is the myocardium. This strong muscle tissue powers the heart's pumping action.
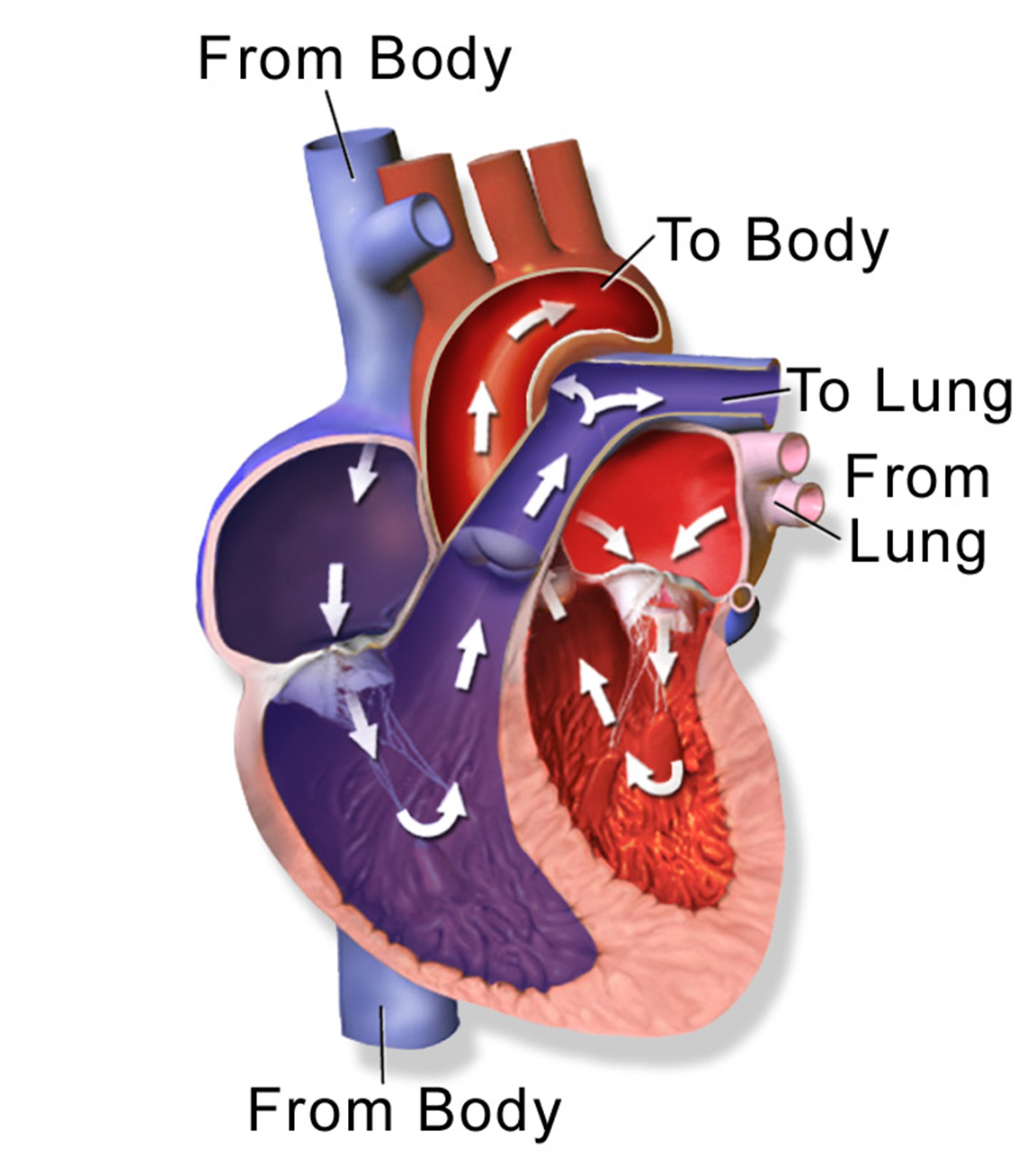
17.6 Circulation Through the Heart Biology LibreTexts
Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. Your heart contains four muscular sections ( chambers) that briefly hold blood before moving it. Electrical impulses make your heart beat, moving blood through these chambers. Your brain and nervous system direct your heart's function. Advertisement.

Muscular Layer of the Heart Wall
The heart is made of three layers of tissue. Endocardium is the thin inner lining of the heart chambers and also forms the surface of the valves.; Myocardium is the thick middle layer of muscle that allows your heart chambers to contract and relax to pump blood to your body.; Pericardium is the sac that surrounds your heart. Made of thin layers of tissue, it holds the heart in place and.

main tissues in the heart
Heart tissue from people with COVID-19 had more macrophages than tissue from controls. More of the macrophages were of the inflammatory type, too. The researchers observed similar results in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2. The team wanted to find out how SARS-CoV-2 infection led to the observed changes in heart macrophages.

Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity · Anatomy and Physiology
As the central part of the circulatory system, the heart is responsible for pumping blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients, and removing metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide from all the tissues.

Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
An electrical stimulus is generated by the sinus node (also called the sinoatrial node, or SA node). This is a small mass of specialized tissue located in the right upper chamber (atria) of the heart. The sinus node generates an electrical stimulus regularly, 60 to 100 times per minute under normal conditions. The atria are then activated.
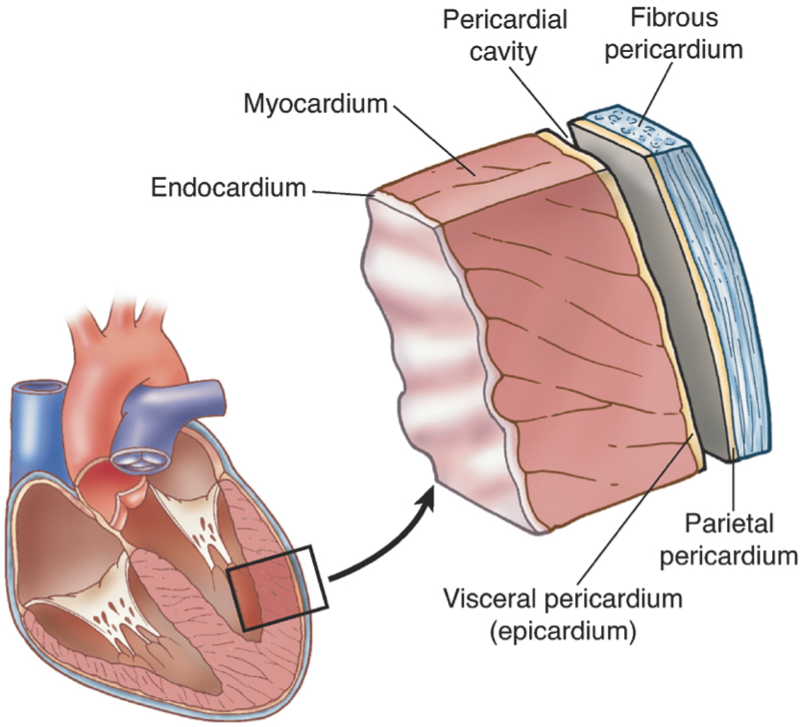
Three Layers Of The Heart slide share
Heart anatomy. The heart has five surfaces: base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. It also has several margins: right, left, superior, and inferior: The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava .

Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
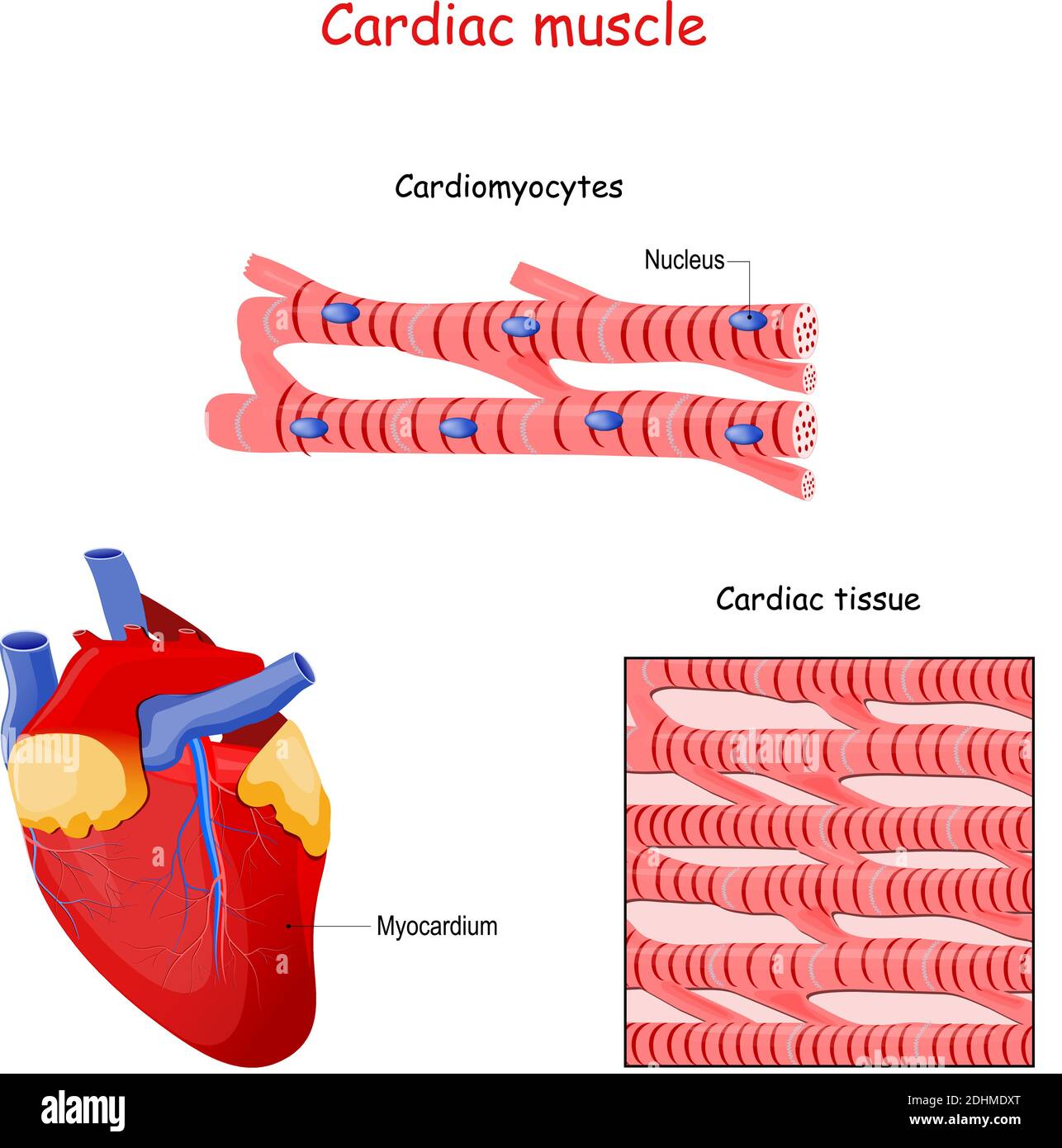
Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. It plays an important role in making your heart beat. We'll go over the unique features of cardiac muscle tissue.

Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart Anatomic Overview and Evaluation of
The heart—the primary organ of the cardiovascular system—is a muscle that contracts regularly, via a natural pacemaker that produces electrical impulses.The heartbeat drives the transport of blood throughout the body, which provides oxygen and nutrients to all the body's cells, tissues, and organs.

Layers of Heart Tissue Stock Image C004/8108 Science Photo Library
The components of the heart's electrical system, including the sinus node (SN) and atrioventricular node (AV node), are illustrated here. You can see the two atria and the two ventricles. Separating them is a layer of fibrous tissue, labeled the AV disc. This tissue keeps the electrical signal passing through the AV node. In this figure: SN.

Describe the Three Layers of the Heart
Cardiac muscle is found in the walls of the heart. It helps the heart perform its function of pumping blood throughout the body. Cardiac muscle tissue is located in the middle of three layers of the heart, called the myocardium . Problems in the myocardium can cause heart failure and arrhythmias or contribute to sudden cardiac death.
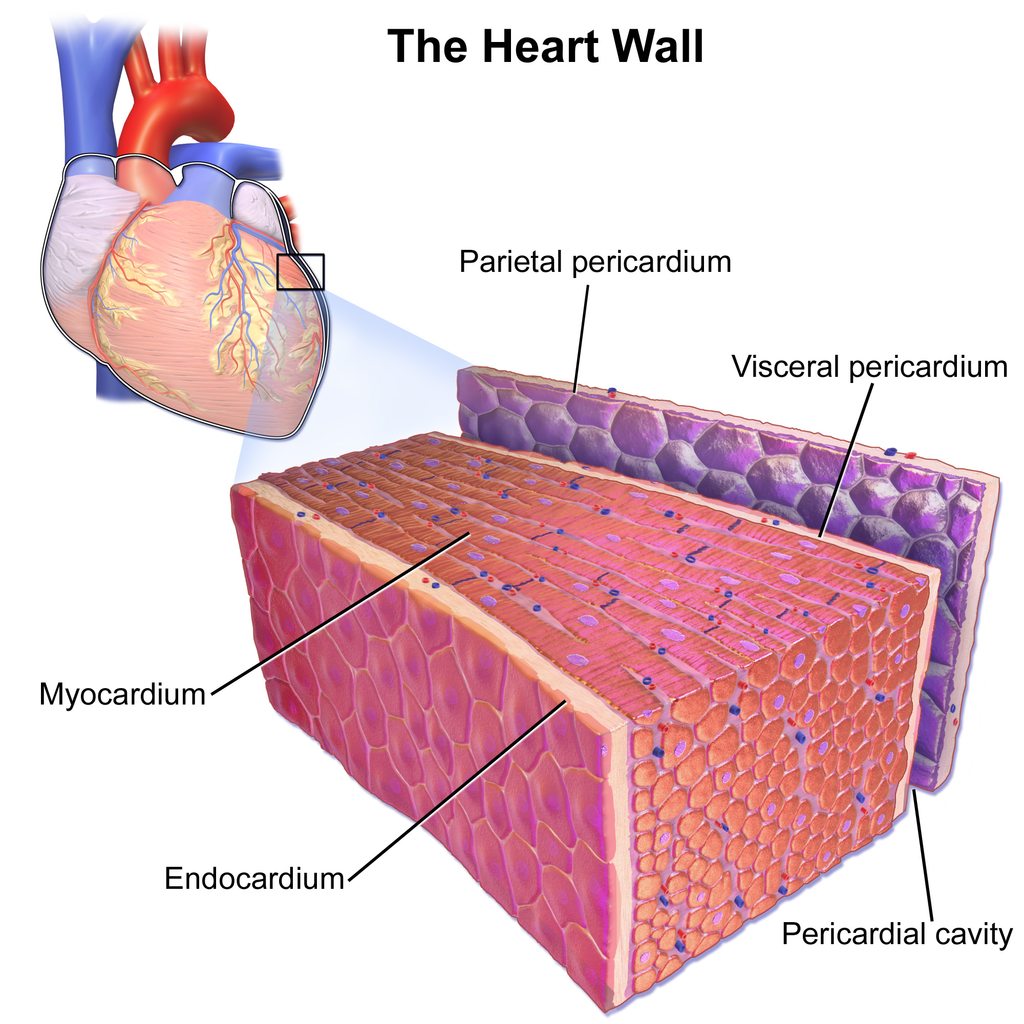
What are the names of three layers of the heart wall? Socratic
Endocardium. The innermost layer of the cardiac wall is known as the endocardium. It lines the cavities and valves of the heart. Structurally, the endocardium is comprised of loose connective tissue and simple squamous epithelial tissue - it is similar in its composition to the endothelium which lines the inside of blood vessels.

Heart Tissues Diagram Quizlet
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is located in the middle cavity of the chest, between the lungs. In most people, the heart is located on the left side of the chest, beneath the breastbone. The heart is composed of smooth muscle. It has four chambers which contract in a specific order, allowing the human.
Cardiac Tissue
The heart beats around 100,000 times a day, pumping approximately 8 pints of blood throughout the body 24/7. This delivers oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to tissues and organs and carries away.
Structure of Cardiac muscle fibers. anatomy of cardiomyocyte
heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.It may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the chambers in the mammalian heart.

heart Structure, Function, Diagram, Anatomy, & Facts Britannica
The parts of the heart conduction system can be divided into those that generate action potentials (nodal tissue) and those that conduct them (conducting fibers). Although all parts have the ability to generate action potentials and thus heart contractions, the sinuatrial (SA) node is the primary impulse initiator and regulator in a healthy heart.