What Are The 5 Layers Of The Earth's Atmosphere? WorldAtlas

Layers of Atmosphere Diagram Quizlet
The top of the mesosphere, called the mesopause, is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures averaging about minus 130 degrees F (minus 90 degrees C) according to the National.

Layers of the Atmosphere Physical Geography
Earth's atmosphere is similar to a jacket for our planet. It surrounds our planet, keeps us warm, gives us oxygen to breathe, and it is where our weather happens. Earth's atmosphere has six layers: the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere, the ionosphere, and the exosphere.. (This is only part of the.
What Are The 5 Layers Of The Earth's Atmosphere? WorldAtlas
Composition of Earth's atmosphere by molecular count, excluding water vapor. Lower pie represents trace gases that together compose about 0.0434% of the atmosphere (0.0442% at August 2021 concentrations).Numbers are mainly from 2000, with CO 2 and methane from 2019, and do not represent any single source.. The three major constituents of Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen, and argon.

Layers of Atmosphere and Their Charchterstics Leverage Edu
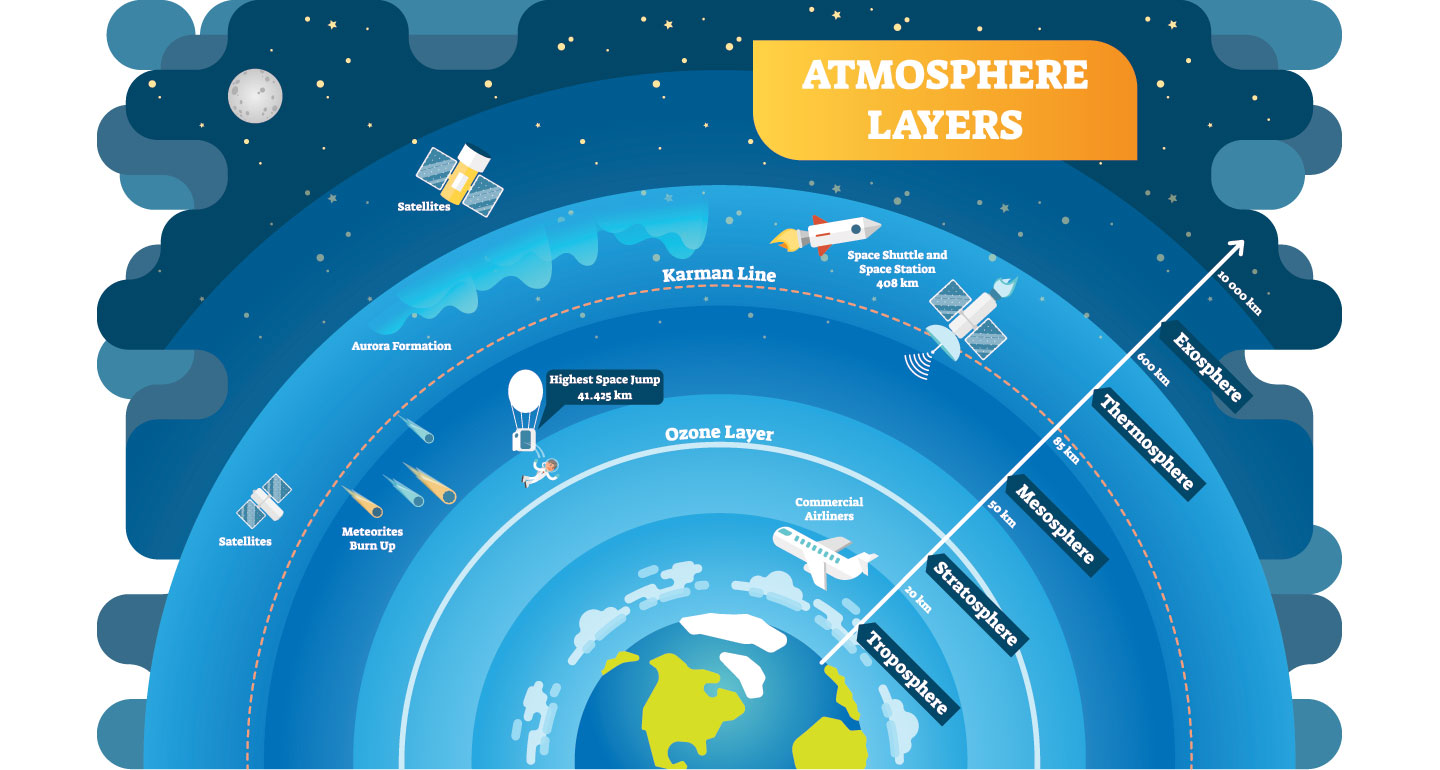
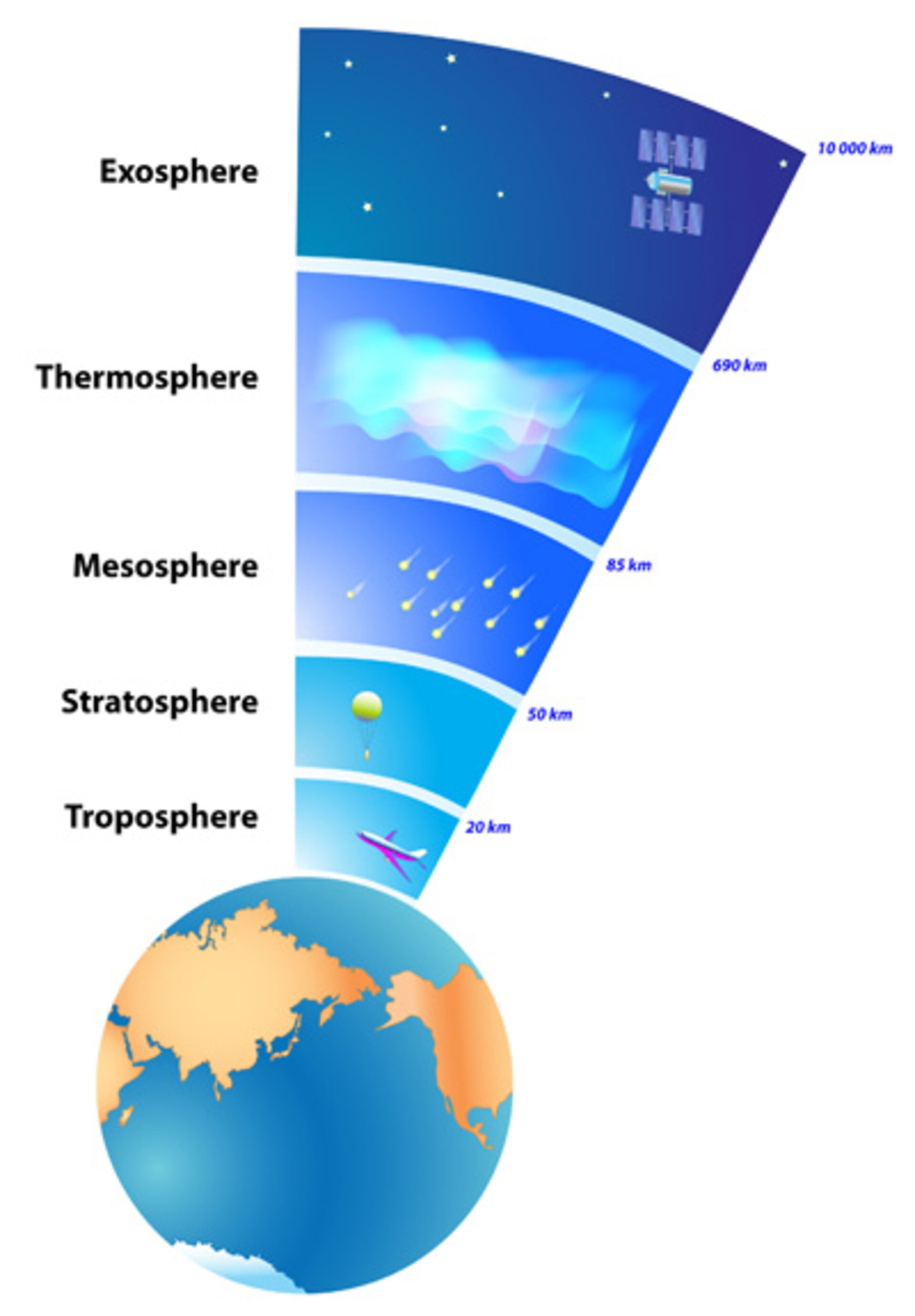
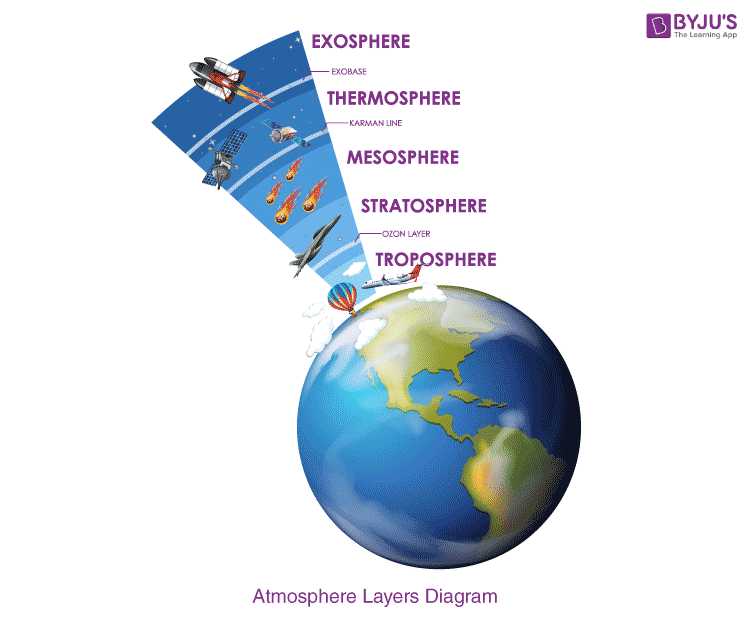
Exosphere. This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. It extends from about 375 miles (600 km) to 6,200 miles (10,000 km) above the earth. In this layer, atoms and molecules escape into space and satellites orbit the earth. At the bottom of the exosphere is a transition layer called the thermopause.
Explainer Our atmosphere — layer by layer
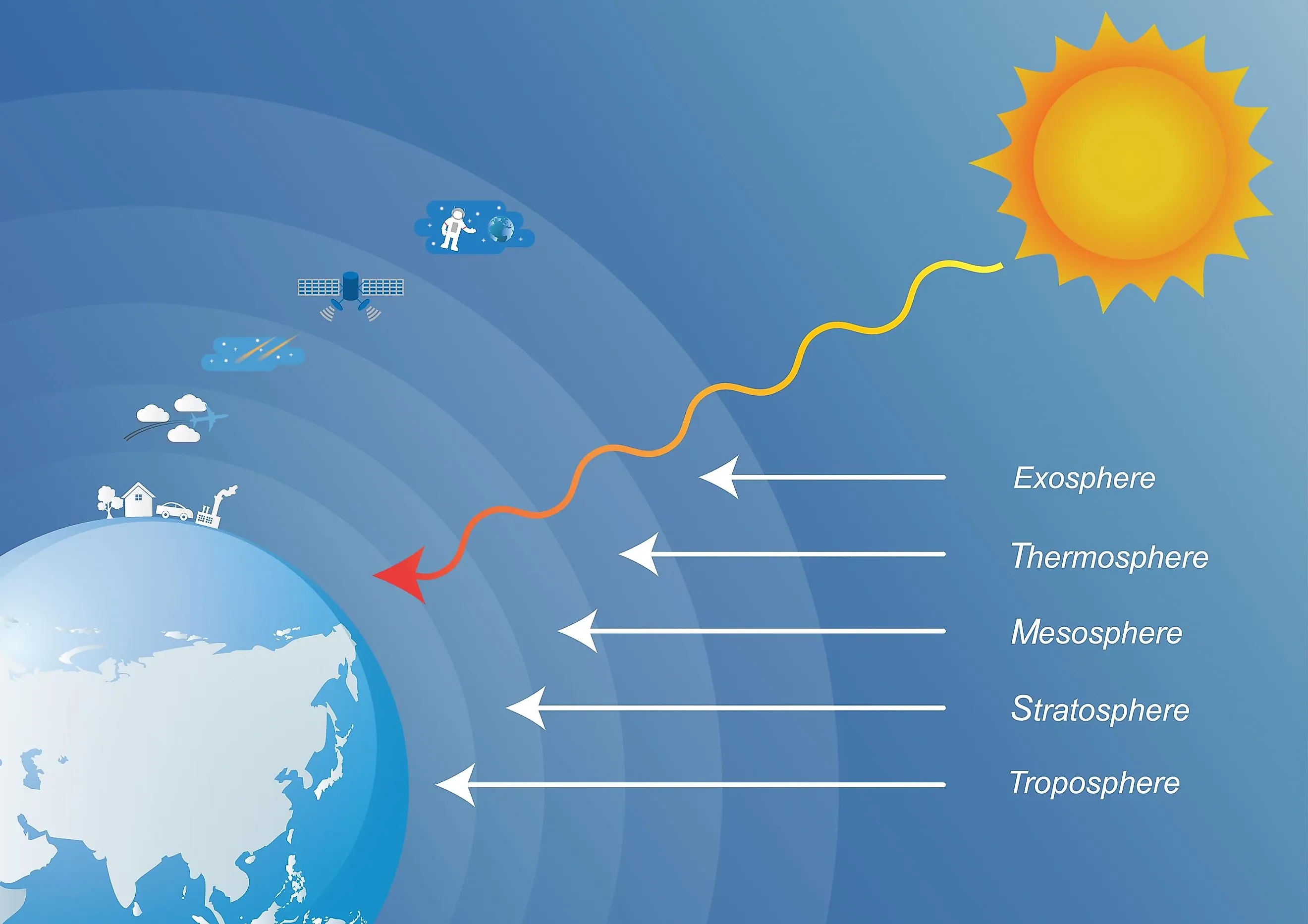
The Earth's layers of atmosphere differ in chemical composition and temperature. They combine to create a protective sheild that maintains our delicate energy balance essential for life on Earth. Most weather occures in the nearest layer, the troposphere (0-7 miles). The stratosphere is the level where jet airliners fly and the ozone layer resides (7-30 miles). Beyondthat is the coldest part.

The Four Spheres Of The Earth WorldAtlas
The Atmosphere. The atmosphere is a layer of gas and suspended solids extending from the Earth's surface up many thousands of miles, becoming increasingly thinner with distance but always held by the Earth's gravitational pull. The atmosphere surrounds the Earth and holds the air we breathe; it protects us from outer space; and holds moisture.

Earth atmosphere structure names on circles Vector Image
This part of the atmosphere is the most dense. Almost all weather is in this region.Stratosphere The stratosphere starts just above the troposphere and extends to 50 kilometers (31 miles) high. The ozone layer, which absorbs and scatters the solar ultraviolet radiation, is in this layer..
Atmospheric circulation Understanding Global Change
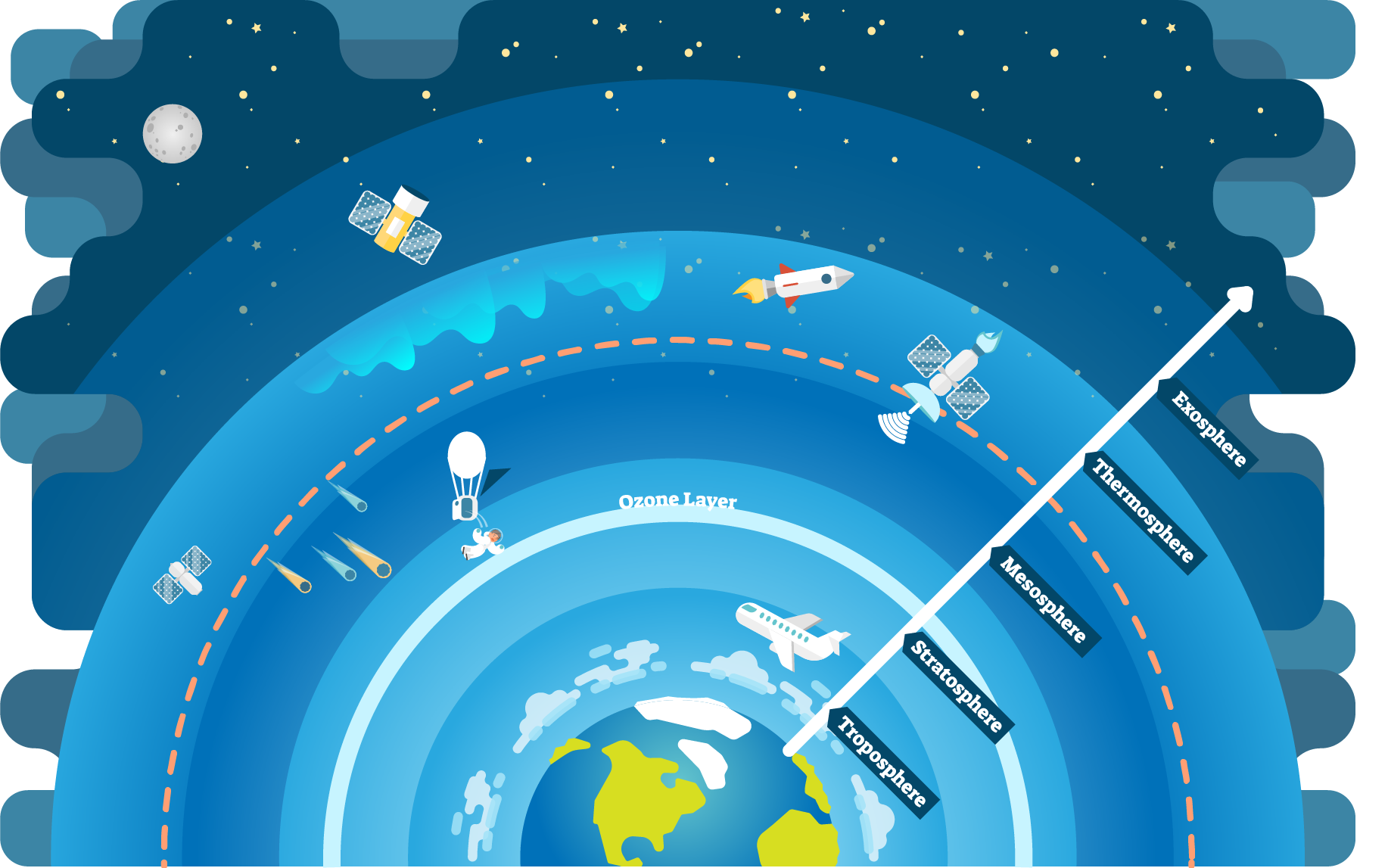
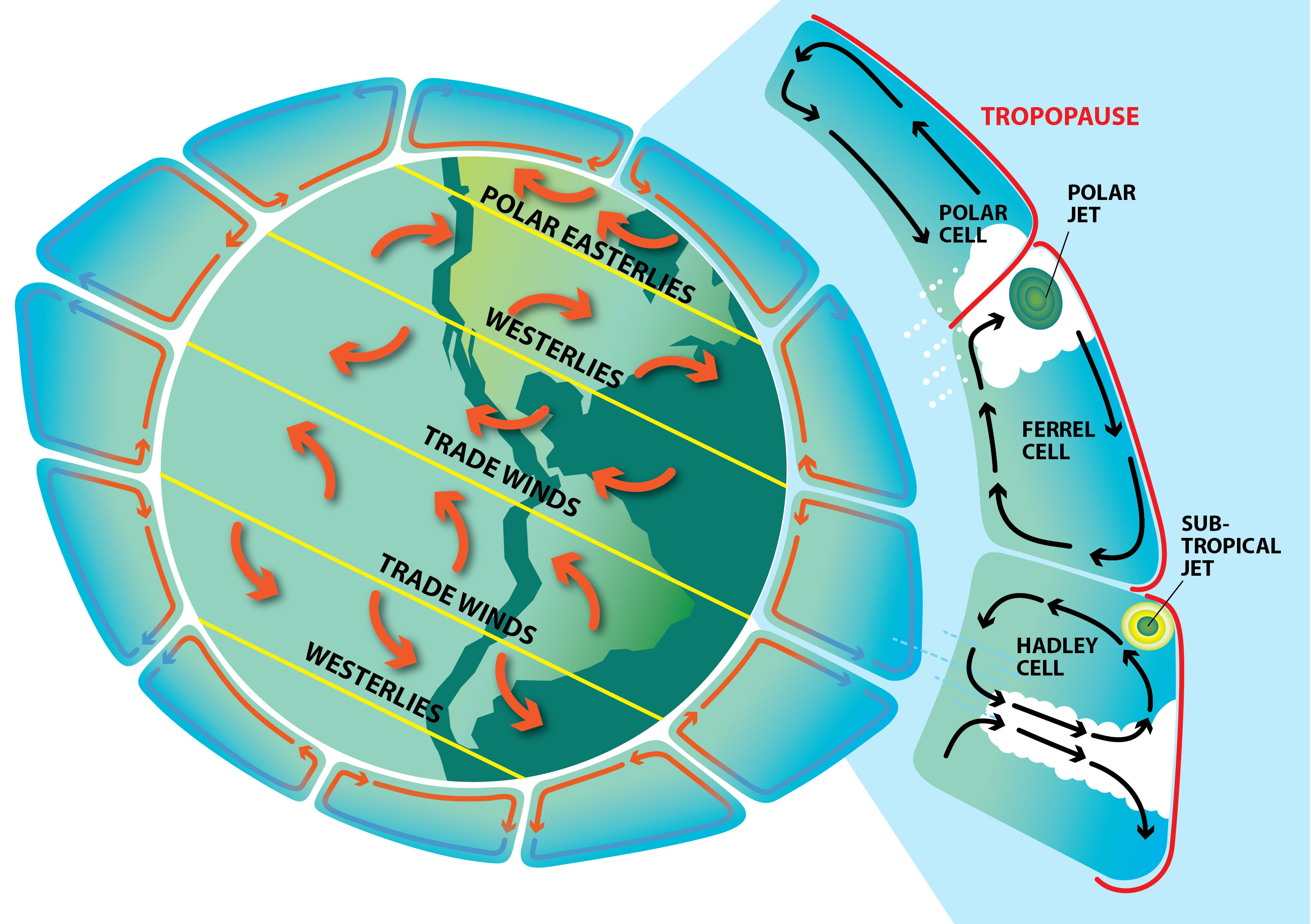
Earth's atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. From lowest to highest, the major layers are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. Troposphere. Earth's troposphere extends from Earth's surface to, on average, about 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) in height, with its height lower at Earth's.
Atmospheric circulation Understanding Global Change
It is a very active part of the atmosphere. It grows and shrinks depending on the energy it absorbs from the Sun. Noctilucent clouds. Noctilucent clouds are the highest clouds in Earth's atmosphere — much higher than your average thunderstorm cloud. They are only visible at night and form when water vapor freezes around dust from meteors.

A Comprehensive Review of the Earth's Atmosphere (Video)
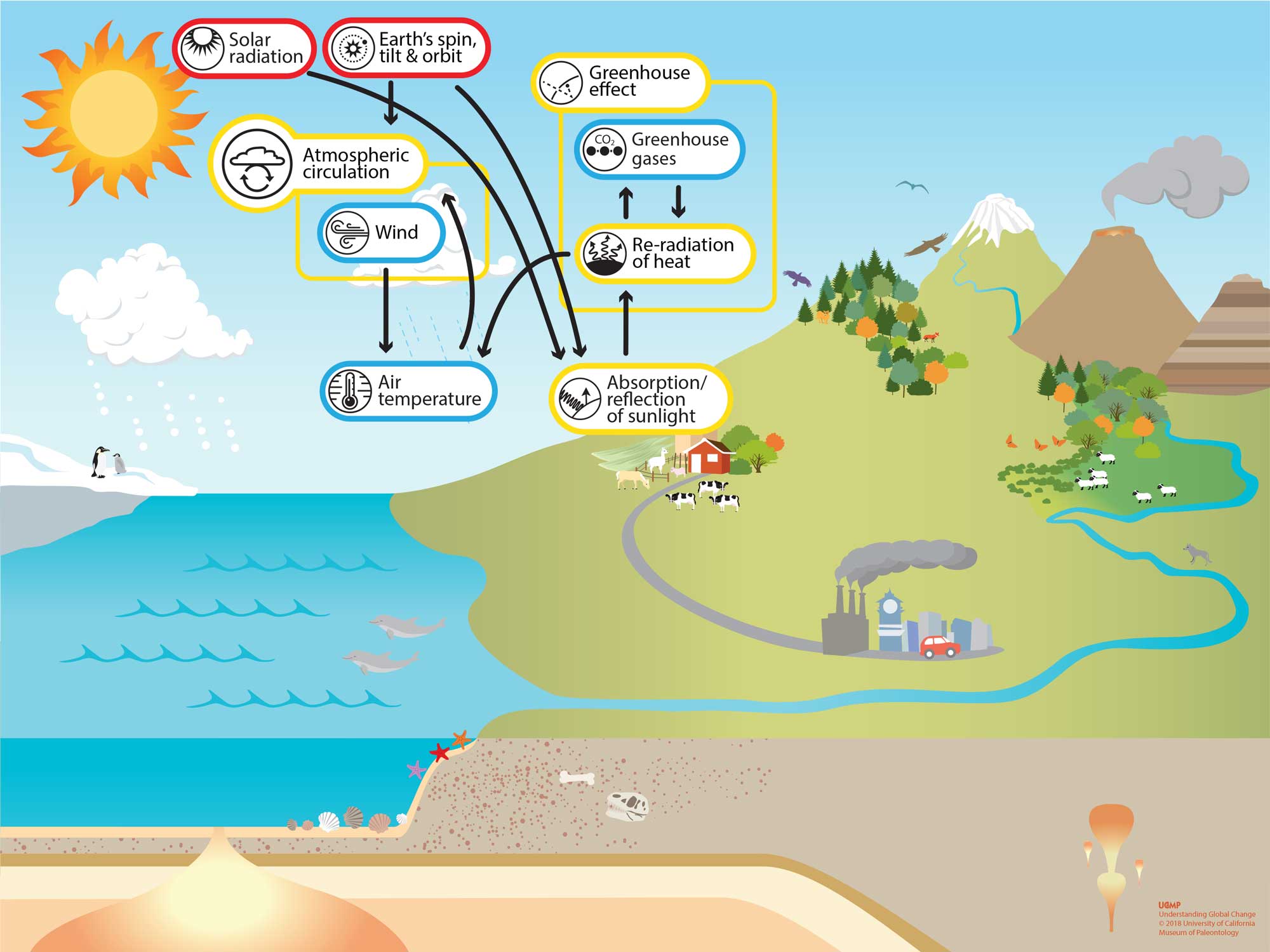
atmosphere, the gas and aerosol envelope that extends from the ocean, land, and ice -covered surface of a planet outward into space. The density of the atmosphere decreases outward, because the gravitational attraction of the planet, which pulls the gases and aerosols (microscopic suspended particles of dust, soot, smoke, or chemicals) inward.

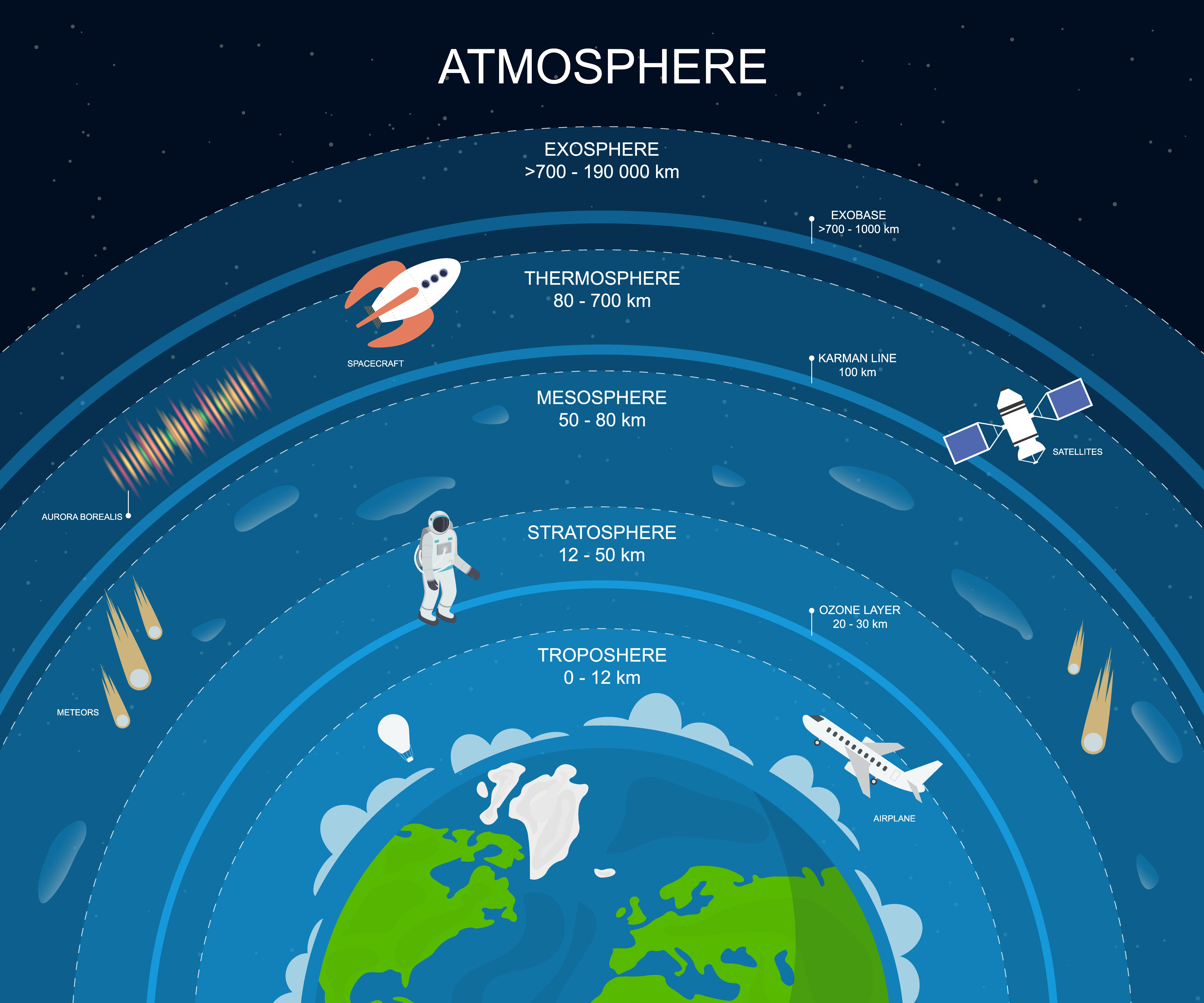
Layers of The Atmosphere Structure of Earth’s Atmosphere
Earth is surrounded by a mixture of gases called the atmosphere. The composition of the atmosphere is 78 %. . nitrogen and 21 %. . oxygen, with the remaining 1 %. . consisting of water vapor, argon, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Earth's atmosphere consists of five distinct layers that are distinguished by.
ESA Layers of Earth's atmosphere
Vocabulary. We live at the bottom of an invisible ocean called the atmosphere, a layer of gases surrounding our planet. Nitrogen and oxygen account for 99 percent of the gases in dry air, with argon, carbon dioxide, helium, neon, and other gases making up minute port ions. Water vapor and dust are also part of Earth 's atmosphere.

Layers earth atmosphere infographics Royalty Free Vector
Earth's Atmosphere News & Articles See All News. Article. 4 Min Read. Can Volcanic Super Eruptions Lead to Major Cooling? Study Suggests No. Article. 7 Min Read. PACE Mission's Sujung Go: Helping Humanity and the Environment. Article. 4 Min Read. Armstrong Flight Research Center: A Year in Review.

Different Layers of the Atmosphere Overview & Structures Video
Composition of Atmosphere - Gases in the Atmosphere. The atmospheric composition of gas on Earth is largely conducted by the by-products of the life that it nurtures. Dry air from earth's atmosphere contains 0.038% of carbon dioxide, 20.95% of oxygen, 78.08% of nitrogen and 0.93% of argon. Traces of hydrogen, neon, helium, nitrous oxide.
Geography Atmosphere Level 2 activity for kids PrimaryLeap.co.uk
A diagram of the layers of Earth's atmosphere. An atmosphere (from Ancient Greek ἀτμός (atmós) 'vapour, steam', and σφαῖρα (sphaîra) 'sphere') [1] is a layer of gasses that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of.
Layers of The Atmosphere Structure of Earth’s Atmosphere
The atmosphere becomes thinner (less dense and lower in air pressure) the further it extends from the Earth's surface. It gradually gives way to the vacuum of space. There is no precise top of the atmosphere, but the area between 100-120 km (62-75 miles) above the Earth's surface is often considered the boundary between the atmosphere and space because the air is so thin here.