Atrial Tachycardia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

Atrial Tachycardia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a fast heart rate that starts in the upper chambers of the heart. Some forms of this tachycardia are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT). With atrial or supraventricular tachycardia, electrical signals in the heart's upper chambers occur abnormally.
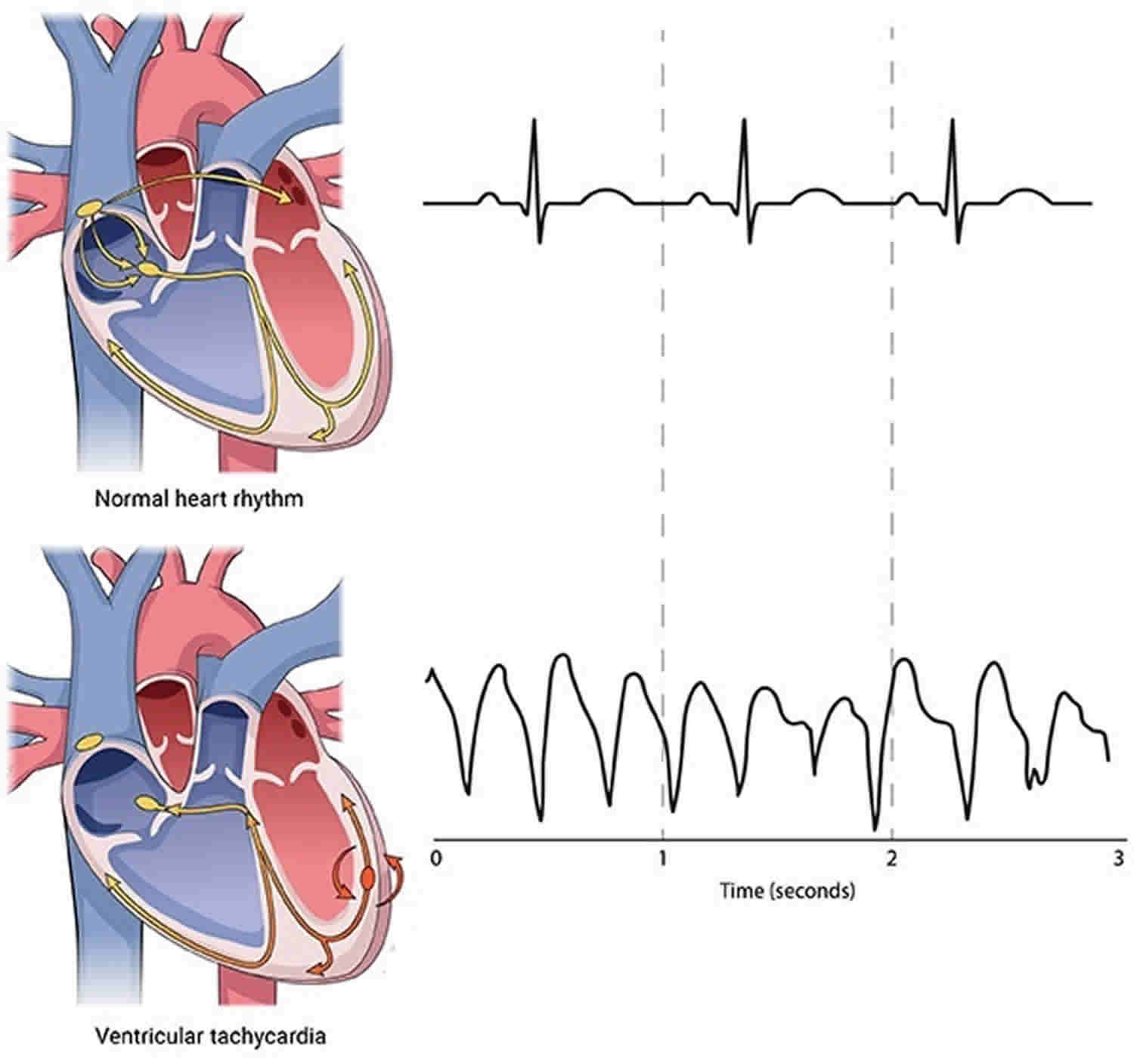
How To Prevent Ventricular Tachycardia Goalrevolution0
Practice Essentials. Atrial tachycardia is a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) that does not require the atrioventricular (AV) junction, accessory pathways, or ventricular tissue for its initiation and maintenance. In addition to individuals with heart diseases, including congenital heart disease, atrial tachycardia may also occur in persons.

Practice EKG Strips 367
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers of the heart, rather than from the sinoatrial node, the normal origin of the heart's electrical activity.As with any other form of tachycardia (rapid heart beat), the underlying mechanism can be.
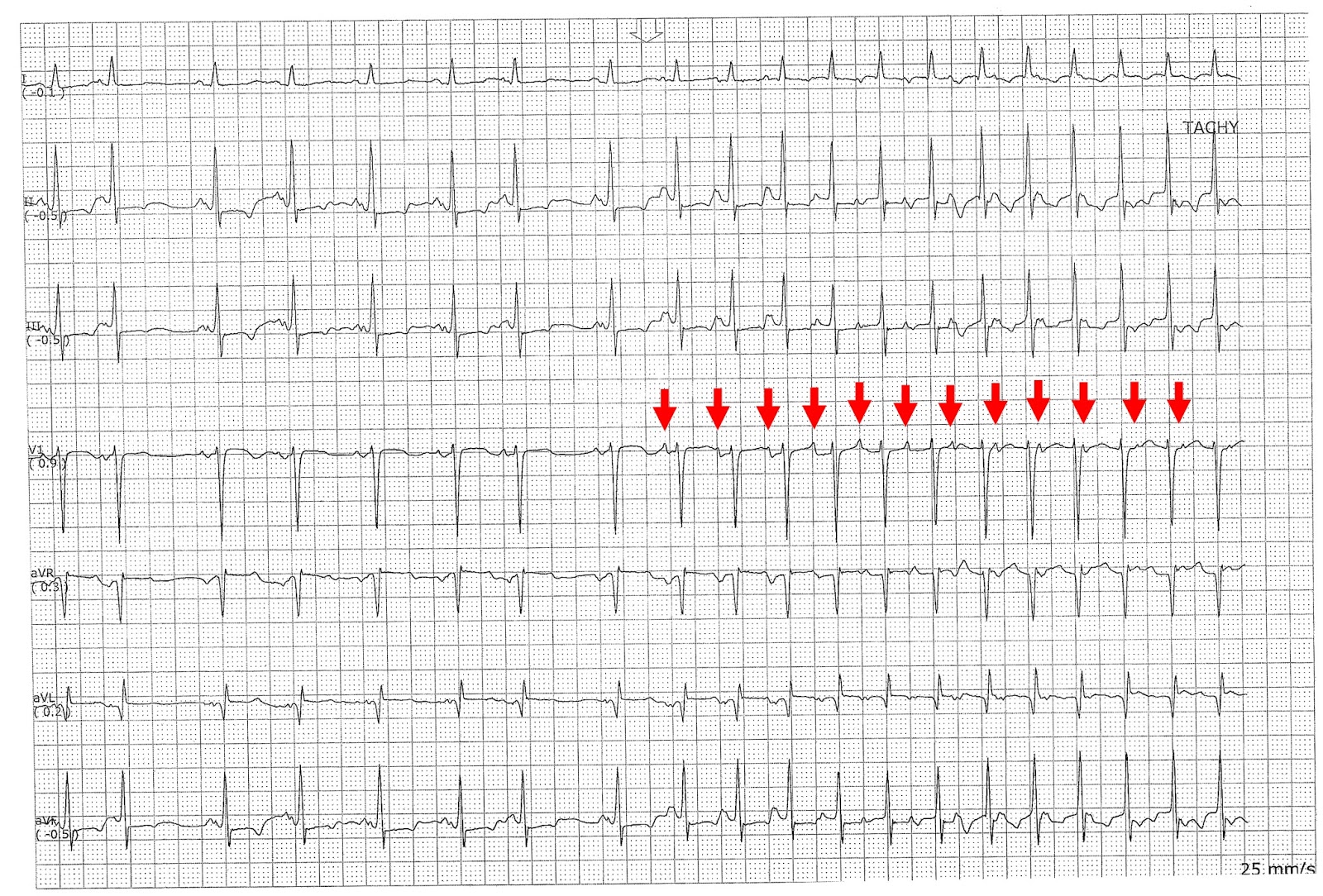
ECG Channel Atrial Tachycardia
410-955-5000 Maryland. 855-695-4872 Outside of Maryland. +1-410-502-7683 International. Atrial tachycardia (AT) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia. It occurs when the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat starts from an unusual location in the upper chambers (atria) and rapidly repeats, causing the atria to beat too quickly.

Differentiating atrial tachycardias with centrifugal activation
N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1438-1448. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMcp1111259. VOL. 367 NO. 15.. Atrial tachycardia is a focal tachycardia that may be a result of a micro-reentrant circuit or an automatic.

Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia —
1438 n engl j med 367;. atrial tachycardia are only slightly faster than these baseline rates. The rhythm is irregular, and on . of medicine n engl j med 367;15 nejm.org october 11, 2012 10.
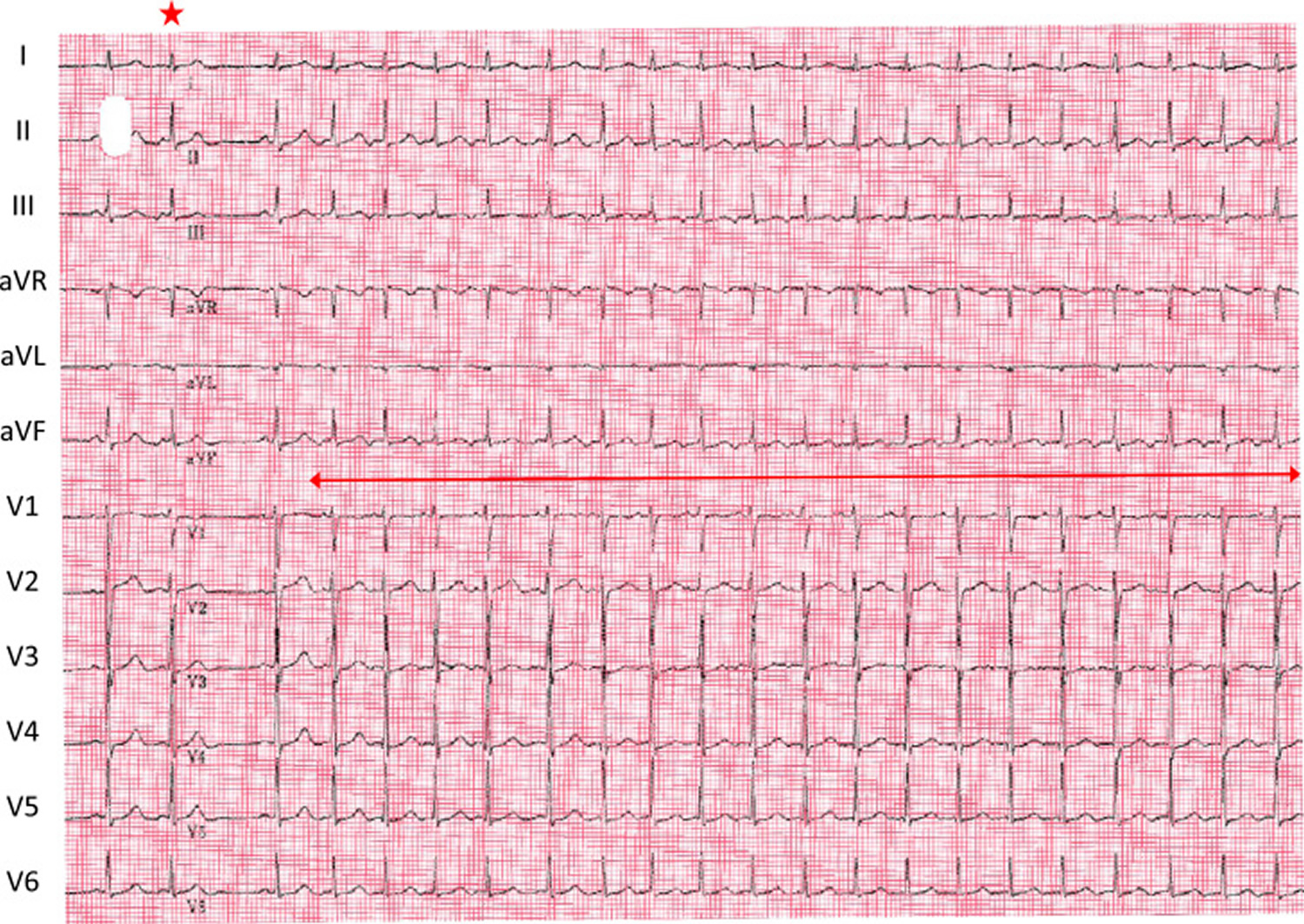
Atrial Tachycardia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Atrial tachycardia (AT) is a regular atrial rhythm at a constant rate of >100 beats per minute originating outside of the sinus node ( waveform 1) [ 1 ]. Focal ATs (also referred to as atrial ectopic tachycardias) arise from a single site within the left or right atrium, in contrast to macroreentrant atrial arrhythmias (eg, atrial flutter) and.

Focal Atrial Tachycardia EKG Interpretation MEDZCOOL YouTube
Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT) is a form of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) originating from a single ectopic focus within the atria but outside of the sinus node. Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT): Consistent, abnormal P wave morphology indicating an ectopic focus. The term FAT is commonly used synonymously with atrial tachycardia, a broader.

Multifocal (or multiform) atrial tachycardia (MAT) GrepMed
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a fast heart rate that starts in the upper chambers of the heart. Some forms of this tachycardia are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT). With atrial or supraventricular tachycardia, electrical signals in the heart's upper chambers occur abnormally.

Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment The Cardiology Advisor
Atrial tachycardia (AT) may be encountered in a variety of settings in the electrophysiology laboratory. It constitutes a differential diagnosis in patients presenting for an electrophysiological evaluation and ablation for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. 1 These patients typically do not have any evidence of structural heart disease. . Patients may also present with AT in setting of.

Atrial tachycardias Thoracic Key
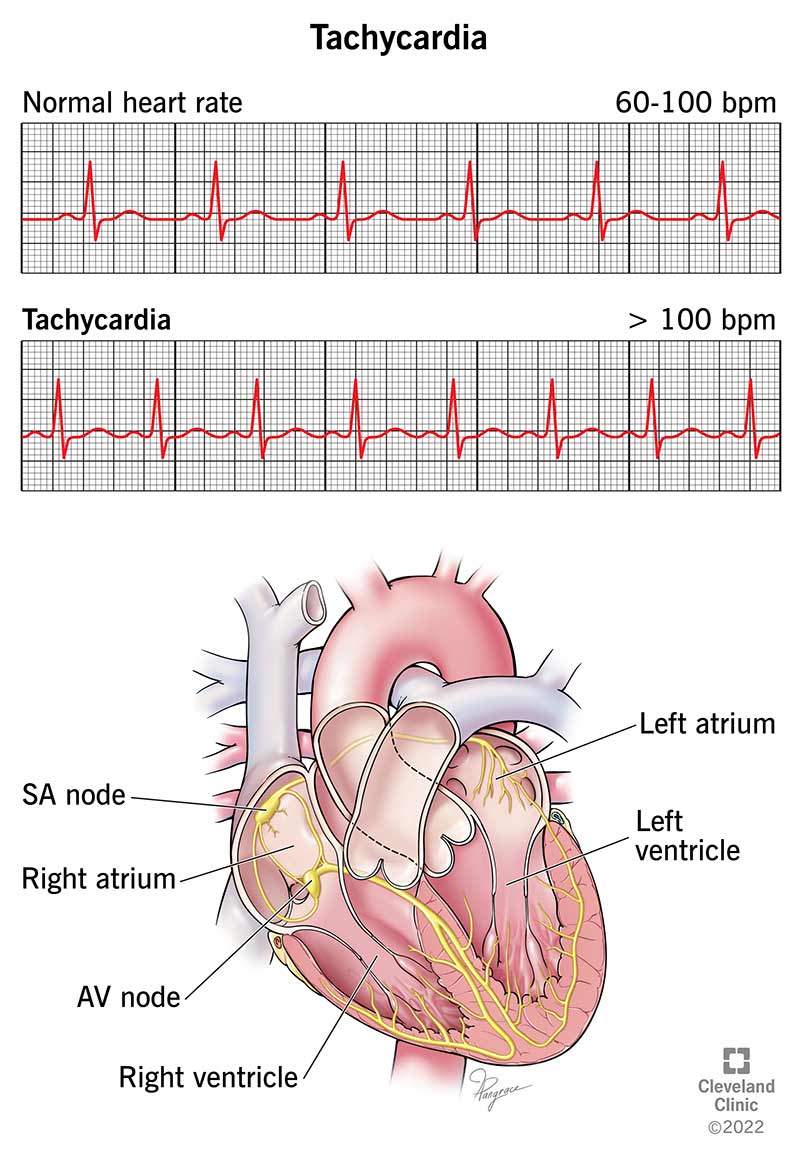
Atrial tachycardia is a fast heartbeat, called an arrhythmia. It's a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). During an atrial tachycardia episode, the heart beats more than 100 times a minute. Then it returns to a heart rate of around 60 to 80 beats a minute. An episode may start slowly or it may start suddenly and quickly.

Atrial tachycardia with 11 atrioventricular conduction precipitated by
Atrial tachycardia is caused by a problem in the heart's conduction system which coordinates the heartbeat. The issue in atrial tachycardia is the heart is beating too fast. Patients can experience this event with or without symptoms. Common symptoms include palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness and passing out.

Treatment for Atrial Tachycardia in Washington DC & Maryland
Atrial tachycardia is an arrhythmia with electrical impulses originating within the atria. Atrial tachycardia can be a result of one or a combination of the mechanisms leading to arrhythmia: automatic, triggered activity, or reentry. In some cases, the mechanism remains undetermined.[1] Electrophysiologic features may overlap if there is a small reentrant circuit, as in micro-reentry. It is.

Atrial tachycardias Thoracic Key
Left atrial tachycardia originating from the mitral annulus-aorta junction. Circulation. 2004; 110:3187-3192. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000147613.45259.D1. Link Google Scholar; 18. Otomo K, Azegami K, Sasaki T, Kawabata M, Hirao K, Isobe M. Successful catheter ablation of focal left atrial tachycardia originating from the mitral annulus aorta.
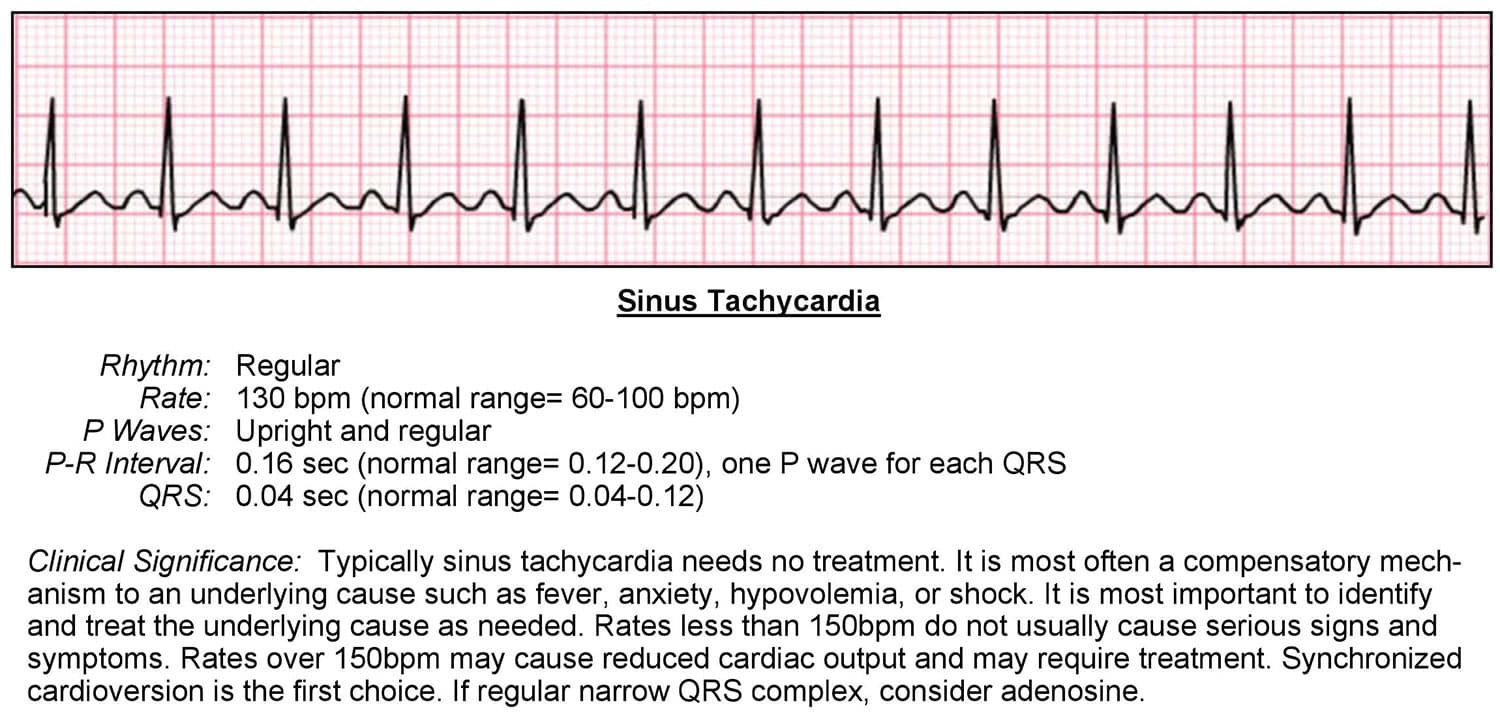
Tachycardia ACLS Wiki
N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1587-1595. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113566. VOL. 367 NO. 17.. atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (in 1 patient), and focal atrial tachycardia (in 1 patient). At 24.
Tachycardia Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Atrial tachycardia is defined as a regular atrial activation from atrial areas with centrifugal spread, caused by enhanced automaticity, triggered activity or microreentry. New ECG classification differentiates between focal and macroreentrant atrial tachycardia.. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2007; 18:367-372. [Google Scholar] 17.